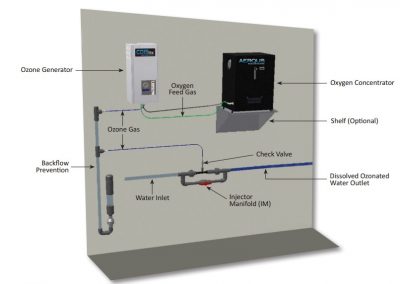
Ozonation
Ozonation
Ozone is made artificially by passing oxygen through ultraviolet light or a “cold” electrical discharge which causes oxygen molecules (O2) to split apart in a process called photolysis. Ozone is also a very strong, broad spectrum disinfectant that is an effective method to inactivate harmful protozoa and also works well against almost all other pathogens. Ozone is used by many municipal drinking water systems to kill bacteria instead of the more common chlorine. Ozonisation is a preferred solution for killing microorganisms in water because it leaves no residue in the water after treatment and has the additional advantages of high oxidation potential, fewer dangerous by-products and the absence of taste and odor problems associated with chlorination.